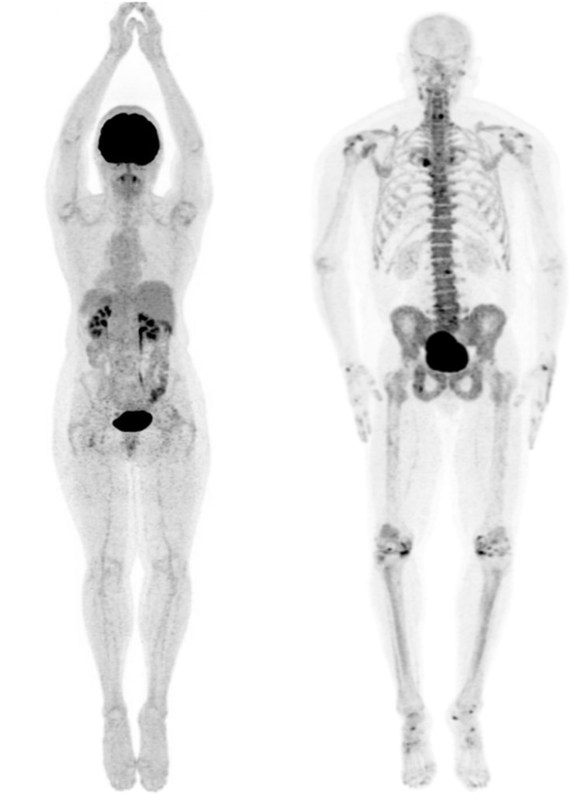
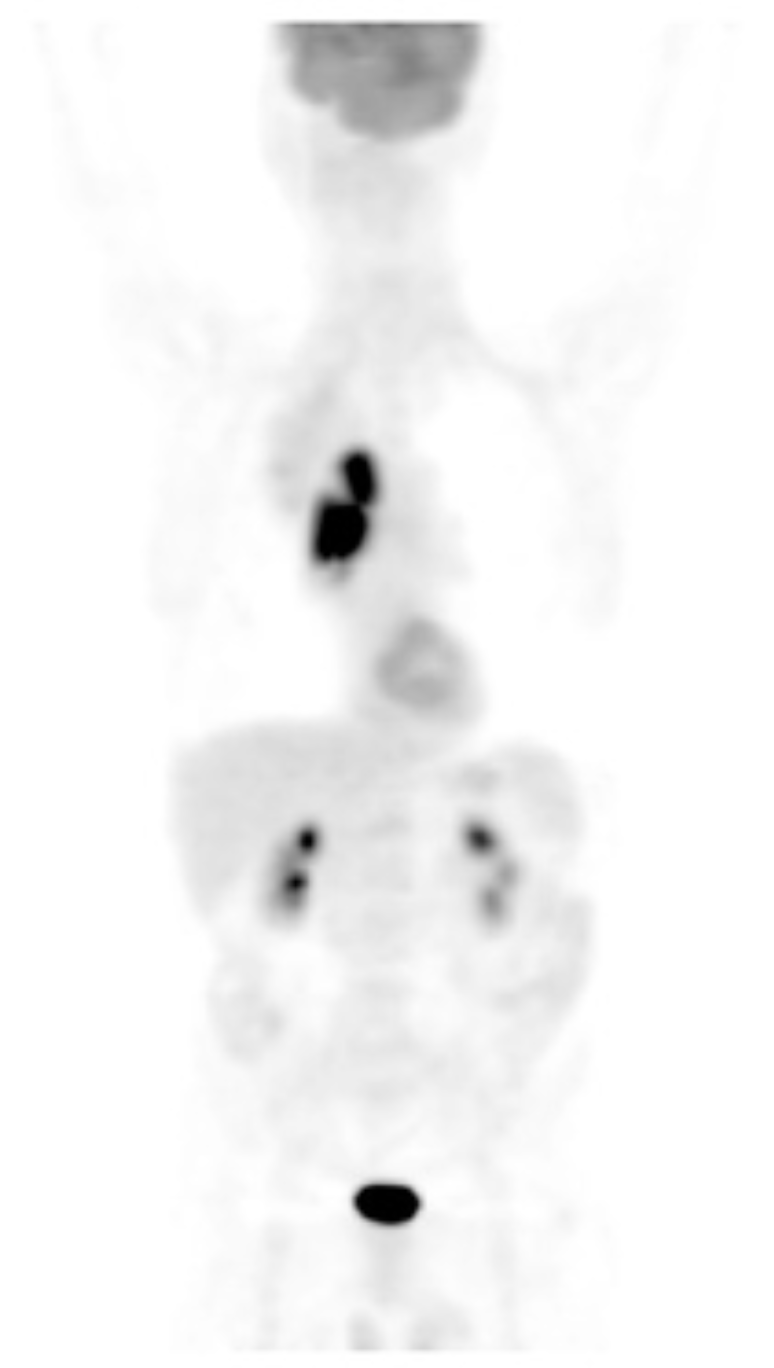
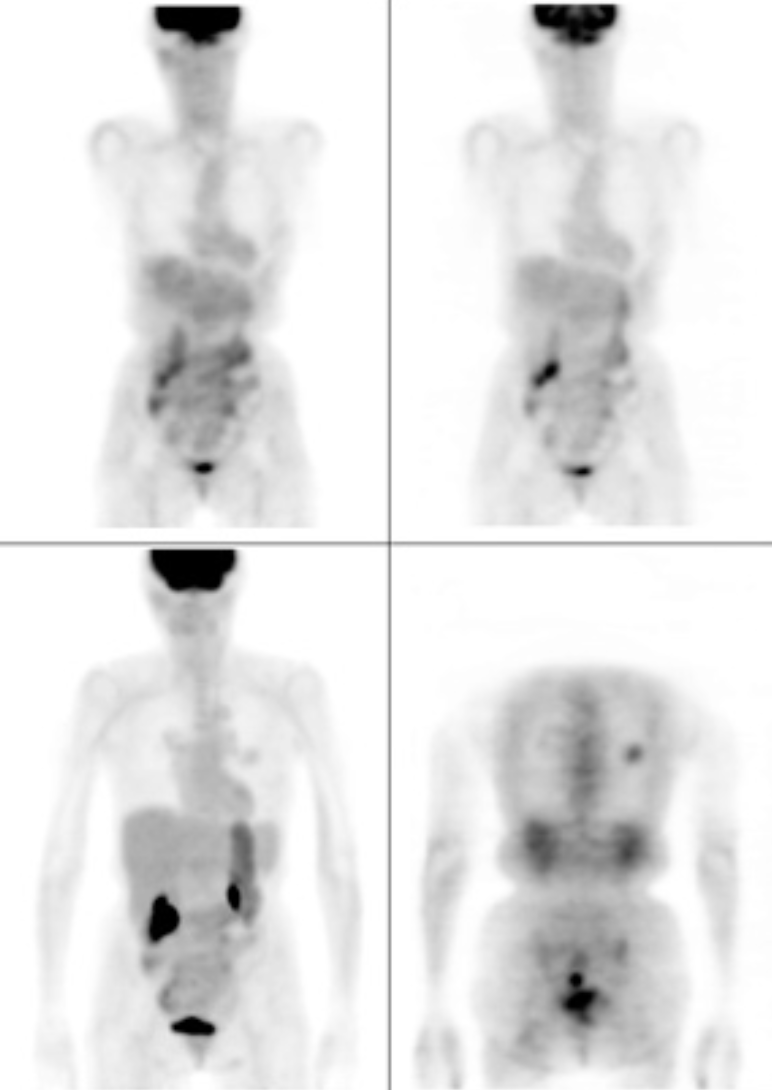
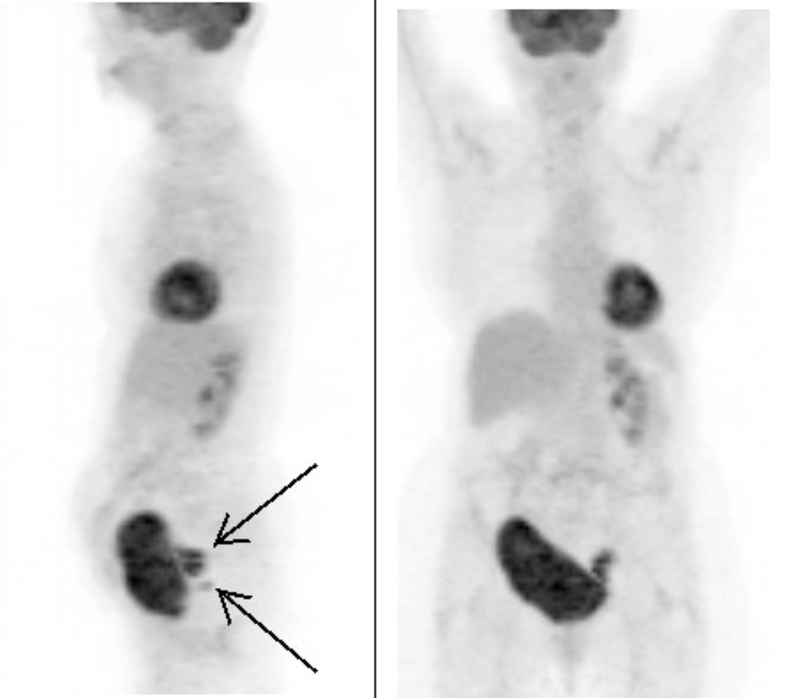
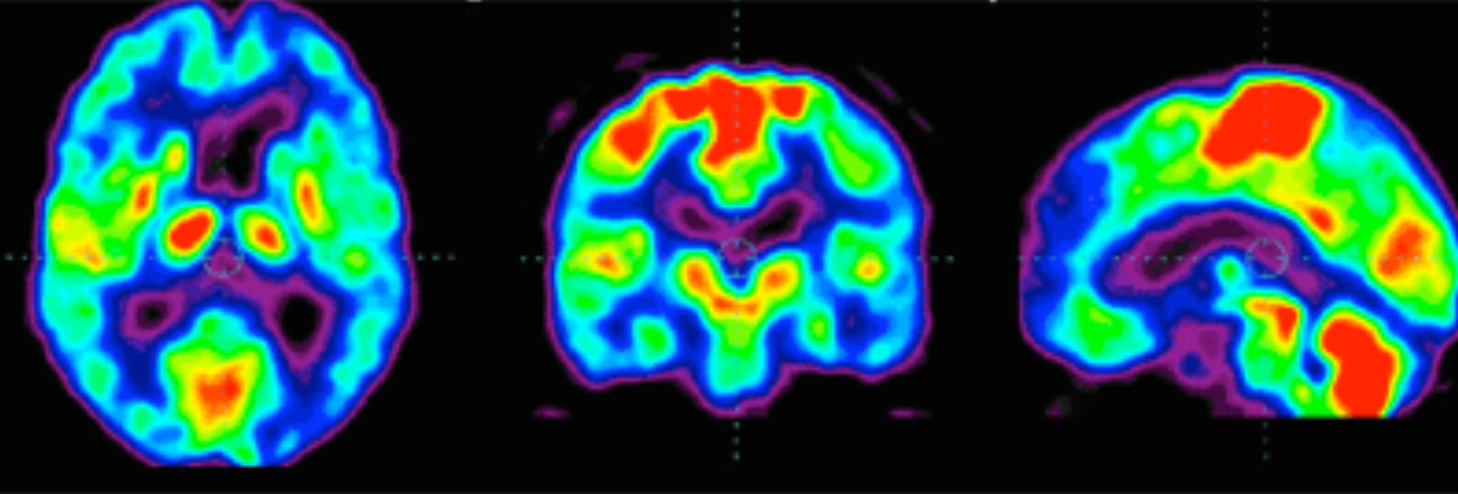
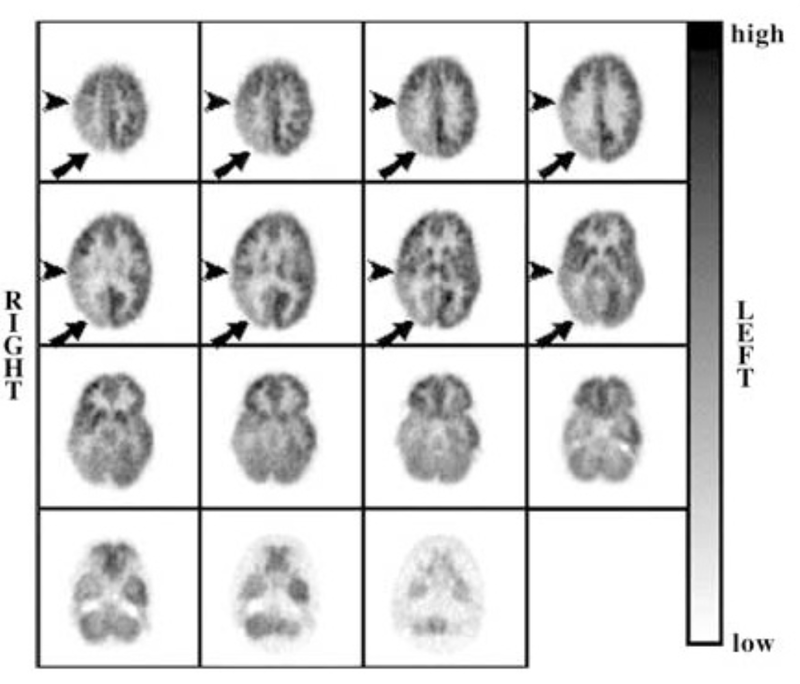
The previously discussed diagnostic tools - ultrasound, X-ray and CT scans - provide structural information of the body, but not much functional information. As we shall see, the PET scan is able to gather functional information, and it does this by detecting the use of glucose.
Glucose is the sugar required for cellular respiration, which is the source of energy for all living cells. If there was a way to measure the amount of glucose being metabolised, we could determine where in the body it is used most.
This is not only useful to measure brain function, the organ that metabolises a lot of glucose, but also places in the body that abnormally metabolises too much glucose, such as tumors.
This is what Positron Emission Tomography does.
Using a radioactive form of glucose (called FDG), and measuring the gamma radiation emitted using a gamma camera, doctors are able to determine glucose use, and thus make functional diagnoses
It is a bit more complex than that.
Glucose is the sugar required for cellular respiration, which is the source of energy for all living cells. If there was a way to measure the amount of glucose being metabolised, we could determine where in the body it is used most.
This is not only useful to measure brain function, the organ that metabolises a lot of glucose, but also places in the body that abnormally metabolises too much glucose, such as tumors.
This is what Positron Emission Tomography does.
Using a radioactive form of glucose (called FDG), and measuring the gamma radiation emitted using a gamma camera, doctors are able to determine glucose use, and thus make functional diagnoses
It is a bit more complex than that.
|
In this video, I discuss Positron Emission Tomography, or PET for short. In particular, I refer to the source of the positron, its annihilation and how the resultant gamma rays are collected. I also briefly discuss its diagnostic benefits. |
|
Click on the images to see diagnoses