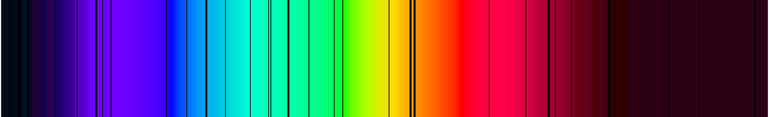
What would you see if you spread the light out from the sun into its various wavelengths?
You might think what we see is this
You might think what we see is this
What we actually get is more like this
The characteristic lines of missing wavelengths actually tell something about the chemical composition of the Sun's surface.
In the late 1600's Sir Isaac Newton was able to show that white light is made up of a number of colours, due to the dispersion of light through a prism.
This eventually lead to a deeper understanding of light - that light could be analysed if you could spread it out into its different wavelengths, whether through the dispersion or diffraction, allowed us learn more about the object in emitting that light.
This eventually lead to a deeper understanding of light - that light could be analysed if you could spread it out into its different wavelengths, whether through the dispersion or diffraction, allowed us learn more about the object in emitting that light.
|
This video examine what spectroscopy is, including absorption and emission spectroscopy and includes a demonstration at the University of Sydney. |
|
Check your understanding
Going Deeper
The question of course is why these lines occur - what are the underlying physics principles?
It was Rydberg and Balmer that were able to identify a mathematical model to the values of the wavelengths that are absorbed or emitted but that still did not provide an full explanation.
It was Niels Bohr that gave us an atomic model that explained these lines, as well as the mathematical models that Rydberg and Balmer discovered. You can learn more at this lesson.
The question of course is why these lines occur - what are the underlying physics principles?
It was Rydberg and Balmer that were able to identify a mathematical model to the values of the wavelengths that are absorbed or emitted but that still did not provide an full explanation.
It was Niels Bohr that gave us an atomic model that explained these lines, as well as the mathematical models that Rydberg and Balmer discovered. You can learn more at this lesson.
Applications
One of the many applications of spectroscopy is the analysis of astronomical information. Go to this lesson to find out more
One of the many applications of spectroscopy is the analysis of astronomical information. Go to this lesson to find out more